Discover Thoughts, Stories, and Experiences
Sharing genuine moments and ideas that inspire

Sharing Life’s Stories and Personal Reflections
A personal blog dedicated to sharing thoughts, experiences, and stories that inspire and connect readers on a meaningful level.

Blog
Dive into a collection of personal stories, reflections, and helpful tips designed to engage and motivate every reader.
-
Tren Makanan Sehat yang Membawa Kembali Sayuran ke Meja Kita
Di era modern ini, banyak orang mulai menyadari pentingnya pola makan sehat.…

Discover Stories and Shared Experiences
Join the conversation by subscribing to updates, exploring new posts, or connecting to share your own stories. See how engaging with the blog enriches your perspective.
Inspiring Stories from My Blog Readers
Discover the simple steps to start your journey and enjoy the full benefits of this personal blog.
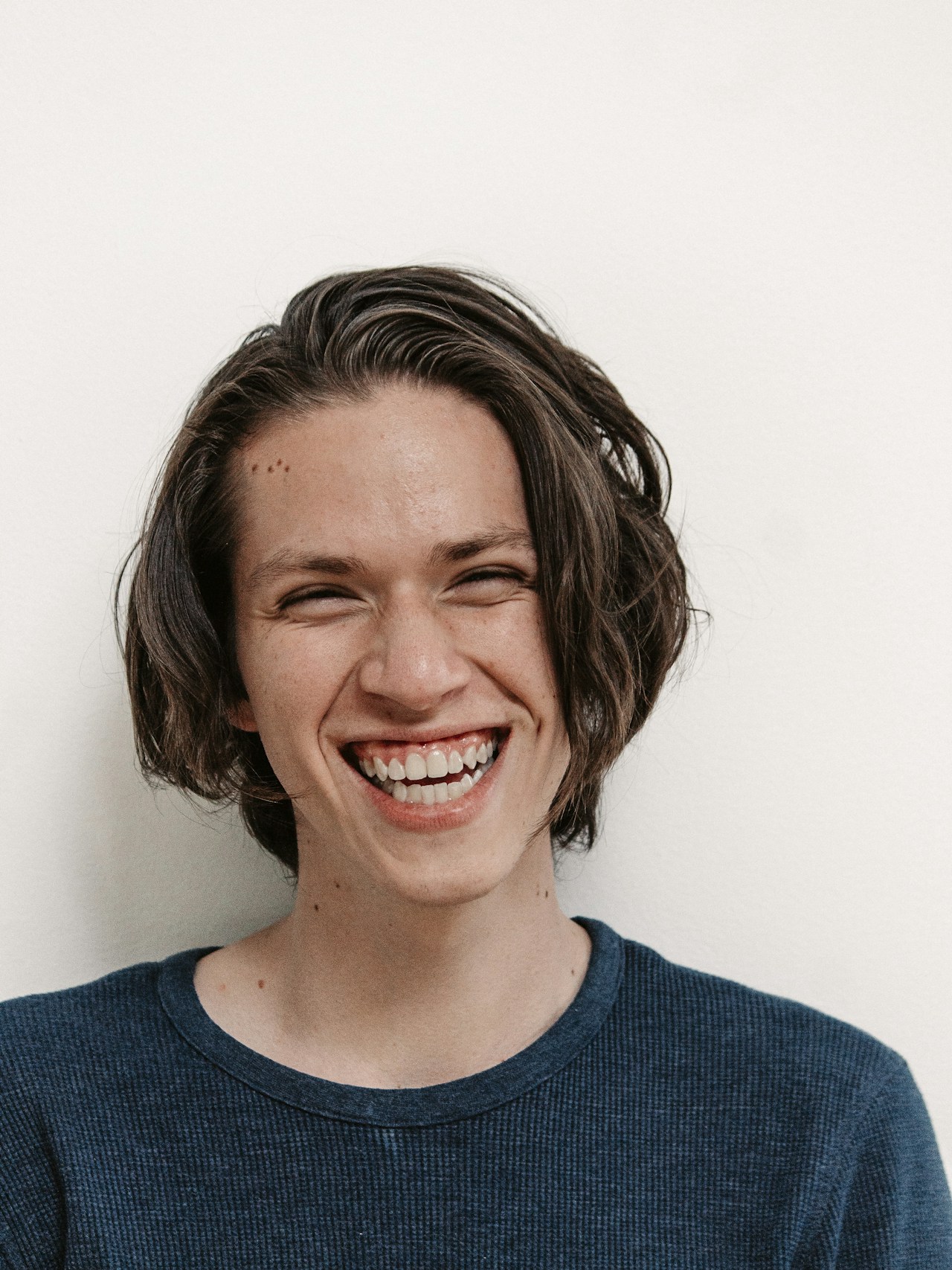

How Sharing Experiences Sparked Personal Growth
This story reveals how sharing personal insights helped deepen connections, inspire others, and grow the blog community.

Sharing Stories That Inspire and Connect
This post demonstrates how thoughtful storytelling can engage readers, build trust, and expand your audience.

Building a Loyal Audience with Authentic Content
This article explains how consistent sharing of genuine experiences led to meaningful engagement and lasting success.
Sharing Thoughts, Experiences, and Stories
Discover key insights and personal reflections that reveal the journey behind each story, highlighting growth, lessons learned, and memorable moments.
250
Blog Posts
5000
Monthly Visitors
120
Subscriber Count
Thoughts to Share and Spark Change
188 Hood Avenue, Apt 305
372 Oak Street, Floor 4
+1-555-321-9876
contact@myblog.com